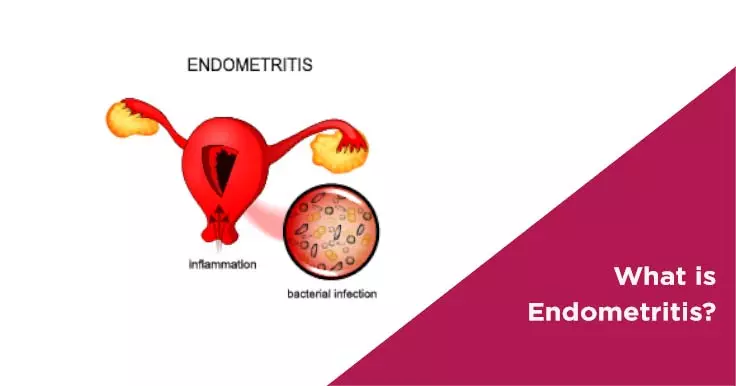
This is not a life-threatening condition but should be treated as soon as possible to prevent complications. If left untreated, Endometritis can cause complications with the functioning of the reproductive organs, infertility and other health issues.
Causes and Risk Factors of Endometritis
Endometritis is usually the result of an infection such as an STD like gonorrhoea or chlamydia, tuberculosis or other bacterial infections. The risk factors for this condition include:
- Childbirth especially through a cesarean delivery or long labor
- Miscarriage
- Any medical procedure that involves the cervix and uterus
- Hysteroscopy
- Dilation and curettage
- Placement of an intrauterine device
Given the risk factors, it is very easy to prevent endometritis by practising safe sex using condoms, getting regularly screened for STDs and ensuring that any surgical procedure needed is performed in a sterile environment with sterile equipment. If you are diagnosed with an STD, take the complete course of treatment as prescribed by the doctor.
Symptoms of Endometritis
Some of the common symptoms associated with this condition are:
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina
- Constipation or discomfort during bowel movements
- Fever
- Pain in the lower abdomen, rectal area or pelvis
Possible Complications of Endometritis
If the infection is not treated in time, it can cause several complications such as:
- Pelvic infection
- Accumulation of pus in the uterus or pelvis
- Infertility
- Septicemia leading to a septic shock
Septicemia and septic shocks can be life-threatening. Thus, they must be treated immediately.
 Infertility Counselling
Infertility Counselling Female Infertility Treatment
Female Infertility Treatment Andrology Treatment
Andrology Treatment Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Female Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male
Fertility Enhancing Surgeries - Male Endoscopy Treatment
Endoscopy Treatment IUI Treatment
IUI Treatment IVF Treatment
IVF Treatment ICSI Treatment
ICSI Treatment Advanced IVF Solutions
Advanced IVF Solutions Embryology
Embryology Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing
Vitrification Egg, Embryo, Sperm Freezing Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm
Donation Program Embryo / Egg / Sperm Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF

 Self-cycleTM IVF
Self-cycleTM IVF